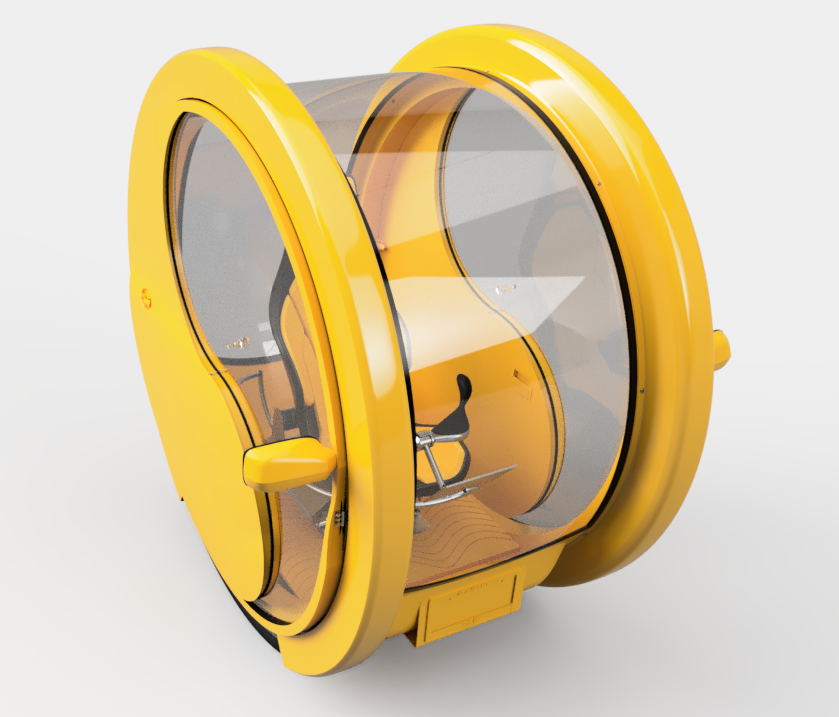
EDI
Description en une ligne : eDI is one of the cheapest and least energy-consuming, enclosed commuter EV with higher maneuverability, performance and braking features than cars and motorcycles.
Description : eDI is an exceptional enclosed commuter EV that redefines the standards of affordability and energy efficiency. It addresses the issue that the daily commute is very expensive, energy-intensive, and stressful for people who live in the agglomeration, but work in the cities. The heavy weight of EVs results in high energy consumption, their large battery and numerous components increase their overall price, and their size makes them inconvenient for parking and difficult to maneuver in busy areas.
Decreasing the size of 4-wheeled cars involves many safety and cost-effectiveness issues, since they focus on the optimization of components of these vehicles. In contrast eDI introduced a new vehicle architecture to reconcile these expectations by closing the gap between cars and diwheels in terms of safety and performance, while maintaining affordability and increasing maneuverability. eDI’s architecture provides solutions to their main engineering challenges including moment of inertia, weight distribution, and unsprung masses by the integration of mechanical, electrical and material engineering researches.
eDI’s innovative technology focuses 100% on lightweight vehicle and powertrain structures. Not only will the eDI offer economic benefits, but it will also have a positive environmental impact. With its lightweight construction, it requires less material during manufacturing, contributing to a reduction in both production costs and carbon emissions. eDI emits 100 g less CO2 per kilometer than the average gasoline car, thus reducing its climate impact.
In addition to its environmental advantages, the eDI offers excellent maneuverability and a small size, making driving less stressful and parking easier. These features enhance the overall commuting experience and further attract potential customers.
Furthermore, the low energy consumption of the eDI plays a significant role in reducing strain on the energy grid. By promoting energy efficiency, the vehicle contributes to a more sustainable and balanced energy consumption pattern.
Lieu d’utilisation/expérimentation : Paris
Geocode the address to put it on the map
Site web : https://ediwheel.com/
Tags : Mobilité électrique, mobilité urbaine, electric-vehicle
Thème : Véhicules intermédiaires, eXtrême Défi, Voiture électrique et charge
Organisations intéressées pour contribuer ou qui contribuent déjà : Ediwheel Ltd
Organisations utilisatrice ou intéressée par utiliser la ressource :
Véhicule(s) impliqué(s) dans le projet : EDI Vehicle
Contributeurs : Áron Ecsenyi
Référent :
Défi auquel répond le projet : Rendre accessible une mobilité individuelle à bas coût pour tous sans externalités négatives
Commun(s) utilisé(s) :
Commun(s) produit(s) :
Communauté(s) d’intérêt associé(s) :
Personnes clés à solliciter :
Niveau de développement : : PMV"PMV" n’est pas dans la liste (Idée, Produit Minimal Viable, POC et 1er client, Présérie, Disponible mais non validé, Disponible et validé, Annulé) de valeurs autorisées pour la propriété "Develop".
Lien vers l’espace de discussion :
Lien vers le salon chat :
Lien vers l’outil de gestion des actions :
Lien vers l'espace de partage de fichiers, documentation :
Besoins : To continue with the physical development of the prototype, we are seeking a pre-seed investment of EUR 70,000, complemented by contributions from our consortium partners.
Complément : Our startup team is now cooperateing with 5 other companies in the implementation of the prototype with the involvement of the Budapest University of Technology and Economics. Based on our CAD designs, we are ready to manufacture the custom components and build the pilot project. The project has undergone analytical and experimental assessments to identify critical functionality and characteristics. The Ediwheel team also developed the manufacturing technology. To do this, we conducted a materials science study, in which the optimal material for the windshield, engine, bearings, and air gap insulator was selected based on the physical characteristics and cost-effectiveness, and then the appropriate machine tools for them.
Prochaine étape :Vous avez des questions ou commentaires sur cette page : Discussion:EDI
Autres informations :
 Français
Français English
English Italiano
Italiano